Blog
How to Engineer Developable Antibodies: AI-Driven Optimization
Dec 22, 2025
You've identified that your antibody has developability liabilities—aggregation at high concentration, high viscosity, or chemical instability. Now what? Abandoning the program means losing millions in investment. Starting over means years of delay while competitors advance.
The solution: Engineer developability into your candidate using AI-driven prediction and rational protein design. Here's the complete workflow, from computational screening to IND filing, with real rescue stories and practical protocols.
Key Takeaways
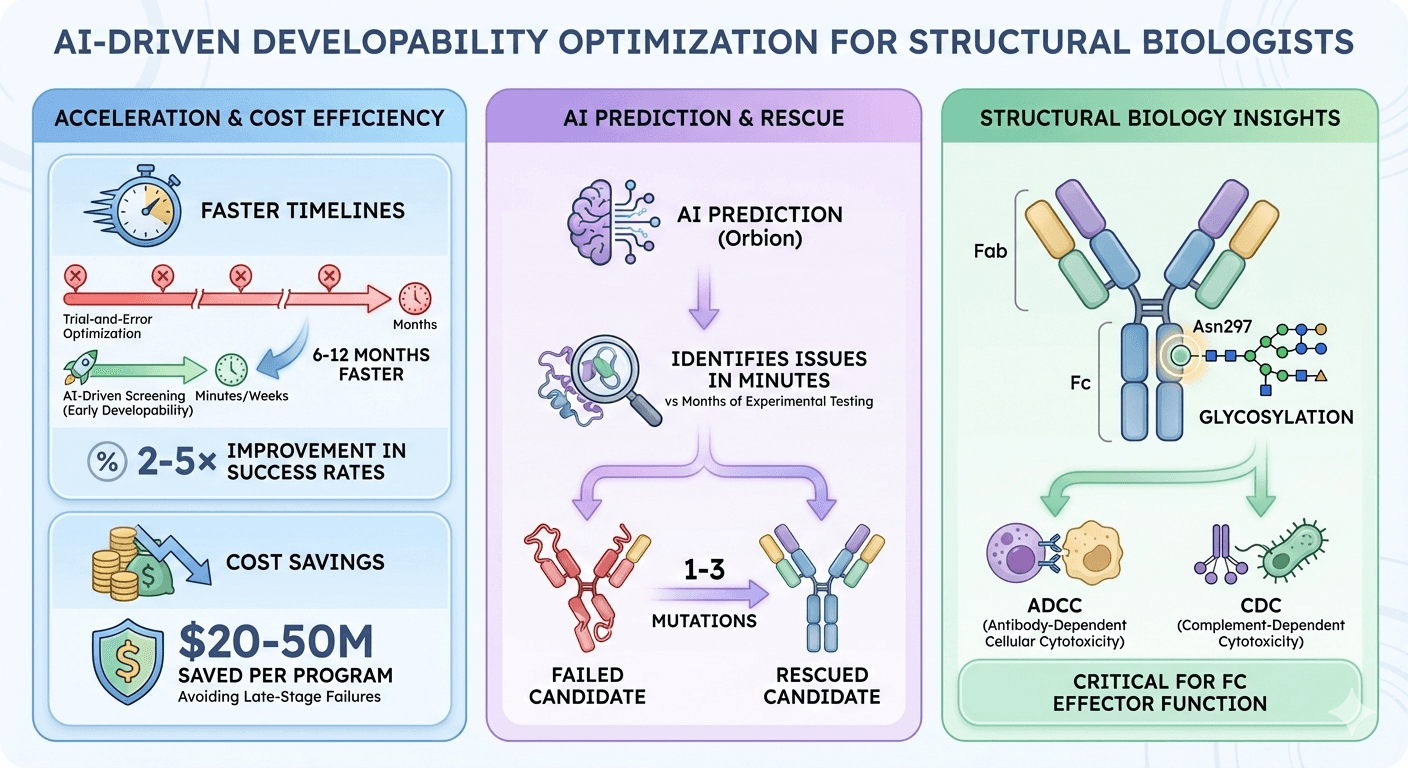
2-5× improvement in success rates with early developability screening
6-12 months faster timelines compared to trial-and-error optimization
$20-50M saved per program by avoiding late-stage failures
AI prediction (Orbion) identifies issues in minutes vs months of experimental testing
1-3 mutations can rescue a failed antibody candidate
Glycosylation at Asn297 is critical for Fc effector function (ADCC/CDC)
The Developability Assessment Workflow
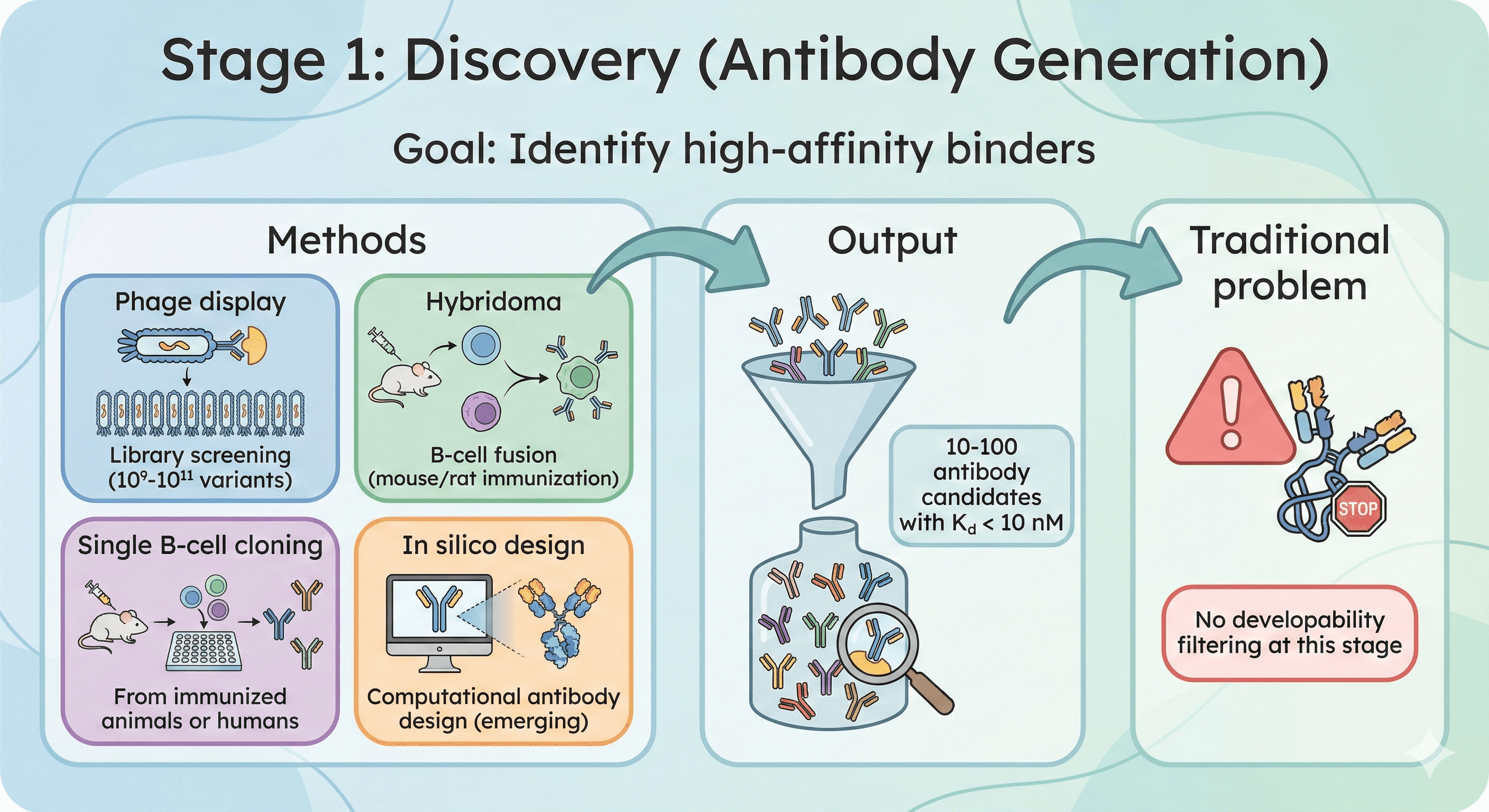
Stage 1: Discovery (Antibody Generation)
Goal: Identify high-affinity binders
Methods:
Phage display: Library screening (10⁹-10¹¹ variants)
Hybridoma: B-cell fusion (mouse/rat immunization)
Single B-cell cloning: From immunized animals or humans
In silico design: Computational antibody design (emerging)
Output: 10-100 antibody candidates with Kd < 10 nM
Traditional problem: No developability filtering at this stage
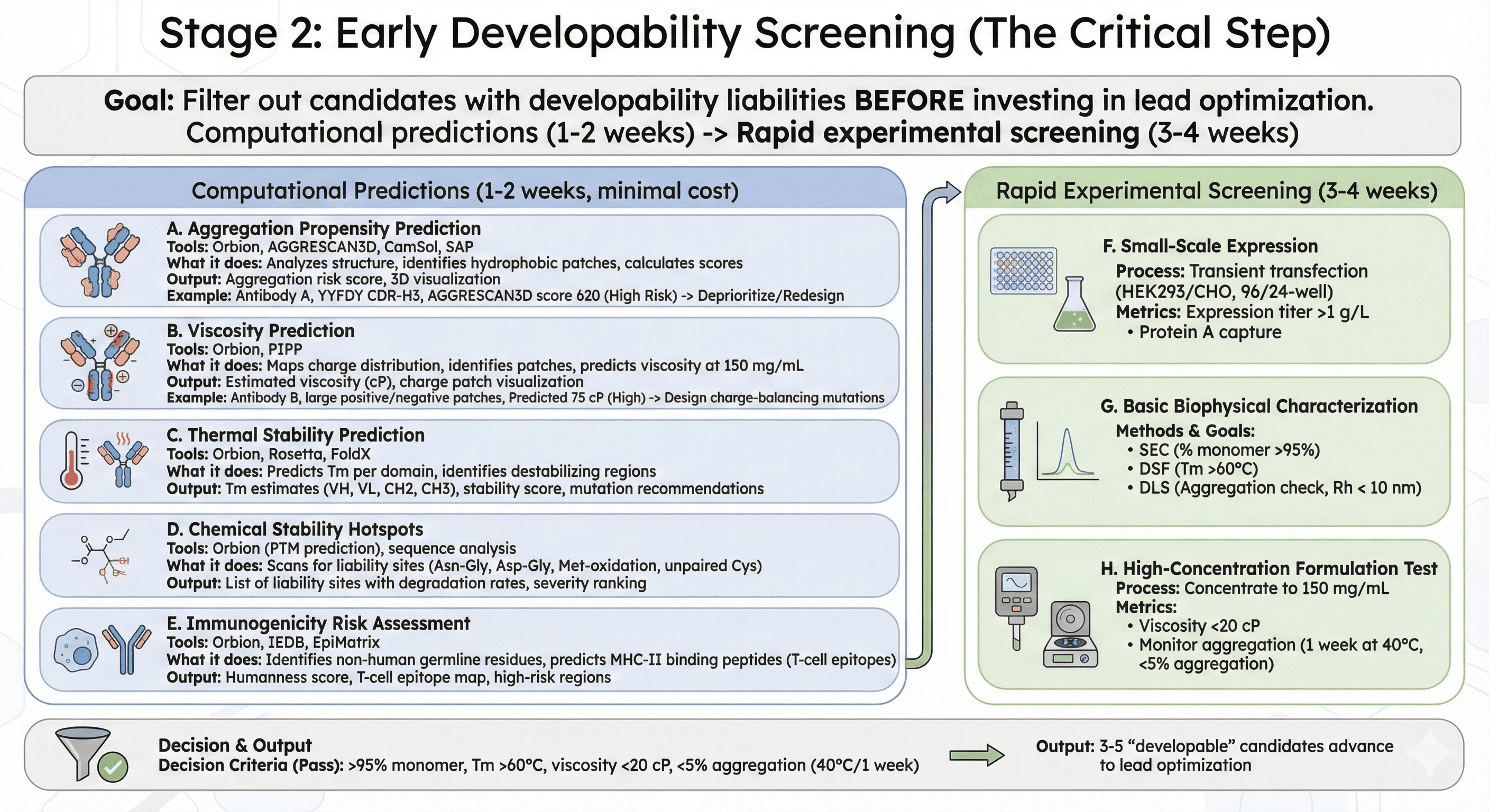
Stage 2: Early Developability Screening (The Critical Step)
Goal: Filter out candidates with developability liabilities BEFORE investing in lead optimization
This is where the new paradigm differs from traditional approaches. Instead of advancing all high-affinity candidates, we computationally predict developability and filter early.
Computational Predictions (1-2 weeks, minimal cost)
A. Aggregation Propensity Prediction
Tools: Orbion, AGGRESCAN3D, CamSol, SAP
What it does:
Analyzes protein structure (AlphaFold or homology model)
Identifies surface-exposed hydrophobic patches
Calculates aggregation propensity score per residue
Highlights hotspot residues in CDRs and frameworks
Output:
Aggregation risk score (low/medium/high)
3D visualization of hydrophobic patches
Specific residues driving aggregation
Example:
Antibody A: CDR-H3 sequence YYFDY (4 aromatic residues clustered)
AGGRESCAN3D score: 620 (high risk, threshold >500)
Decision: Deprioritize or redesign CDR-H3
B. Viscosity Prediction
Tools: Orbion, PIPP (Protein Interaction Property Prediction)
What it does:
Maps charge distribution on antibody surface
Identifies charge patches (positive and negative clusters)
Predicts viscosity at 150 mg/mL using protein-protein interaction models
Output:
Estimated viscosity (cP)
Charge patch visualization
Residues contributing to charge anisotropy
Example:
Antibody B: Large positive patch (7 Lys/Arg) on VH, large negative patch (5 Glu/Asp) on VL
Predicted viscosity: 75 cP (target <20 cP)
Decision: Design charge-balancing mutations
C. Thermal Stability Prediction
Tools: Orbion (ΔΔG predictions), Rosetta, FoldX
What it does:
Predicts melting temperature (Tm) for each domain
Identifies destabilizing mutations or regions
Suggests stabilizing mutations
Output:
Tm estimates for VH, VL, CH2, CH3
Stability score per domain
Mutation recommendations
D. Chemical Stability Hotspots
Tools: Orbion (PTM prediction), sequence analysis
What it does:
Scans for liability sites:
Asn-Gly (deamidation)
Asp-Gly (isomerization)
Met in CDRs (oxidation)
Unpaired Cys (disulfide scrambling)
Output:
List of liability sites with predicted degradation rates
Severity ranking (high/medium/low risk)
E. Immunogenicity Risk Assessment
Tools: Orbion (T-cell epitope prediction), IEDB, EpiMatrix
What it does:
Identifies non-human germline residues
Predicts MHC-II binding peptides (T-cell epitopes)
Scores immunogenicity risk
Output:
Humanness score (% identity to human germline)
T-cell epitope map
High-risk regions for humanization
Rapid Experimental Screening (3-4 weeks)
After computational filtering, test top 10-20 candidates experimentally:
F. Small-Scale Expression
Transient transfection in HEK293 or CHO (96-well or 24-well format)
Expression titer: Goal >1 g/L
Purification: Protein A capture (automated, high-throughput)
G. Basic Biophysical Characterization
SEC (size-exclusion chromatography): % monomer (goal >95%)
DSF (differential scanning fluorimetry): Tm (goal >60°C for all domains)
DLS (dynamic light scattering): Aggregation check (Rh < 10 nm)
H. High-Concentration Formulation Test
Concentrate to 150 mg/mL (spin concentrator)
Measure viscosity (viscometer)
Monitor aggregation: Store 1 week at 40°C (accelerated stability)
Decision criteria:
Pass: >95% monomer, Tm >60°C, viscosity <20 cP, <5% aggregation after 1 week at 40°C
Output: 3-5 "developable" candidates advance to lead optimization
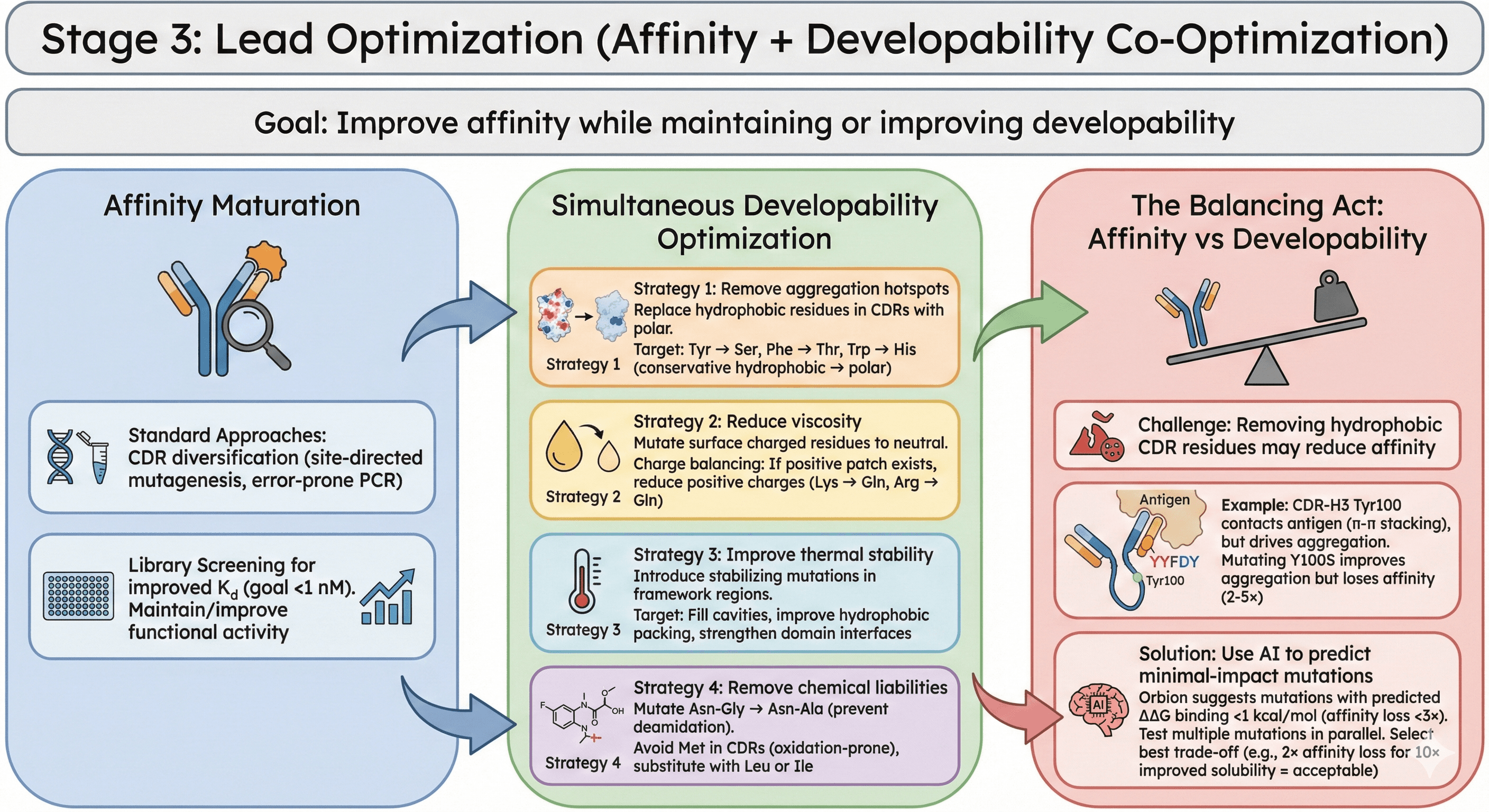
Stage 3: Lead Optimization (Affinity + Developability Co-Optimization)
Goal: Improve affinity while maintaining or improving developability
Affinity Maturation
Standard approaches:
CDR diversification (site-directed mutagenesis, error-prone PCR)
Library screening for improved Kd (goal <1 nM)
Maintain or improve functional activity
Simultaneous Developability Optimization
Strategy 1: Remove aggregation hotspots
Replace hydrophobic residues in CDRs with polar residues
Target: Tyr → Ser, Phe → Thr, Trp → His (conservative hydrophobic → polar)
Strategy 2: Reduce viscosity
Mutate surface charged residues to neutral
Charge balancing: If positive patch exists, reduce positive charges (Lys → Gln, Arg → Gln)
Strategy 3: Improve thermal stability
Introduce stabilizing mutations in framework regions
Target: Fill cavities, improve hydrophobic packing, strengthen domain interfaces
Strategy 4: Remove chemical liabilities
Mutate Asn-Gly → Asn-Ala (prevent deamidation)
Avoid Met in CDRs (oxidation-prone), substitute with Leu or Ile
The Balancing Act: Affinity vs Developability
Challenge: Removing hydrophobic CDR residues may reduce affinity
Example:
CDR-H3 has Tyr100 contacting antigen (π-π stacking with target)
Tyr100 also drives aggregation (exposed hydrophobic patch)
Mutating Y100S improves aggregation but loses affinity (2-5×)
Solution: Use AI to predict minimal-impact mutations
Orbion suggests mutations with predicted ΔΔG binding <1 kcal/mol (affinity loss <3×)
Test multiple mutations in parallel
Select best trade-off (e.g., 2× affinity loss for 10× improved solubility = acceptable)
AI-Driven Optimization with Orbion
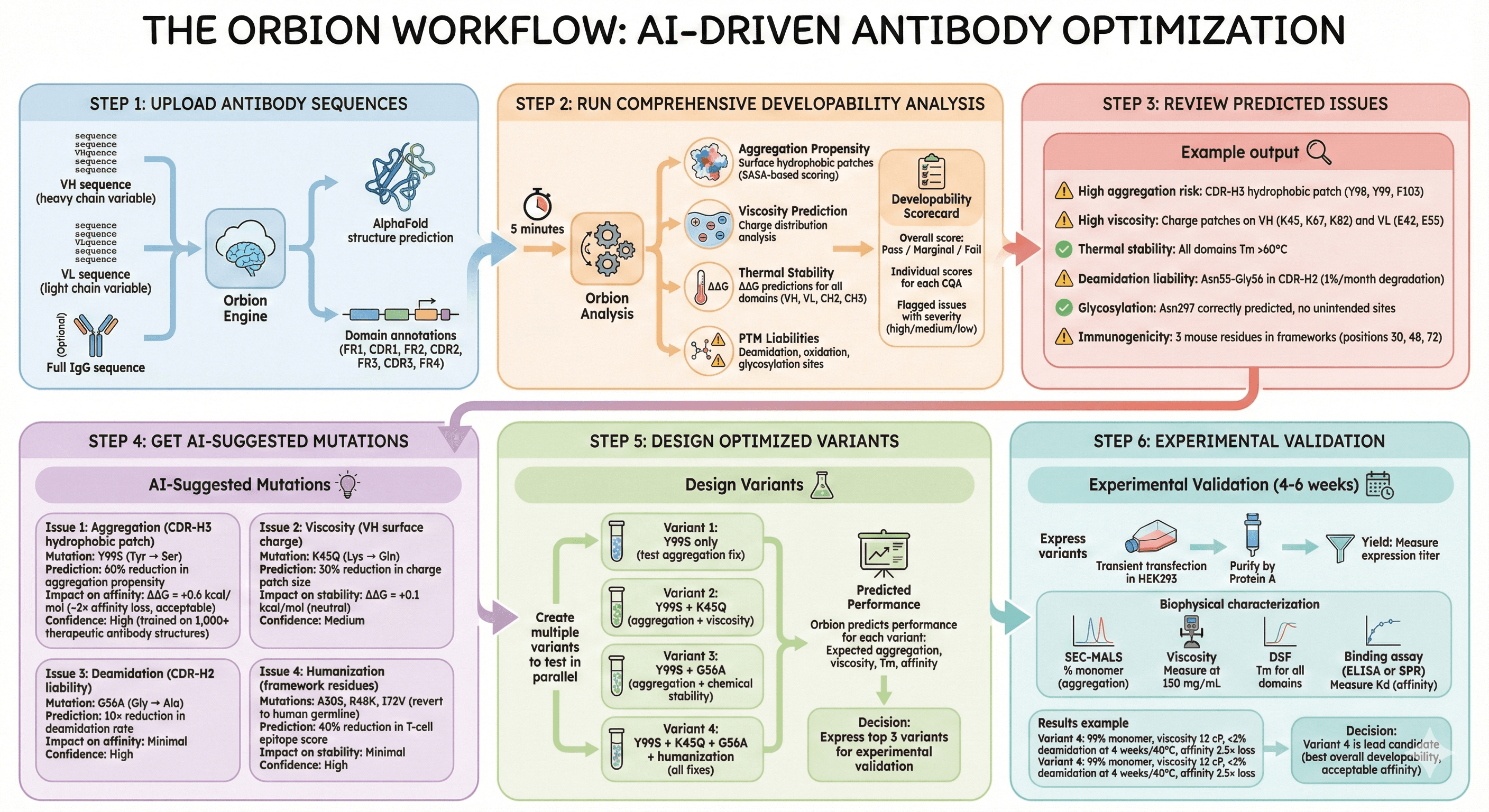
The Orbion Workflow
Step 1: Upload Antibody Sequences
Input:
VH sequence (heavy chain variable region)
VL sequence (light chain variable region)
Optional: Full IgG sequence (includes constant regions)
Orbion generates:
AlphaFold structure prediction (if no experimental structure)
Domain annotations (FR1, CDR1, FR2, CDR2, FR3, CDR3, FR4)
Step 2: Run Comprehensive Developability Analysis
Orbion analyzes (5 minutes):
Aggregation propensity: Surface hydrophobic patches (SASA-based scoring)
Viscosity prediction: Charge distribution analysis
Thermal stability: ΔΔG predictions for all domains (VH, VL, CH2, CH3)
PTM liabilities: Deamidation, oxidation, glycosylation sites
Output: Developability Scorecard
Overall score: Pass / Marginal / Fail
Individual scores for each CQA
Flagged issues with severity (high/medium/low)
Step 3: Review Predicted Issues
Example output:
⚠️ High aggregation risk: CDR-H3 hydrophobic patch (Y98, Y99, F103)
⚠️ High viscosity: Charge patches on VH (K45, K67, K82) and VL (E42, E55)
✓ Thermal stability: All domains Tm >60°C
⚠️ Deamidation liability: Asn55-Gly56 in CDR-H2 (1%/month degradation)
✓ Glycosylation: Asn297 correctly predicted, no unintended sites
⚠️ Immunogenicity: 3 mouse residues in frameworks (positions 30, 48, 72)
Step 4: Get AI-Suggested Mutations
For each issue, Orbion suggests specific mutations:
Issue 1: Aggregation (CDR-H3 hydrophobic patch)
Mutation: Y99S (Tyr → Ser)
Prediction: 60% reduction in aggregation propensity
Impact on affinity: ΔΔG = +0.6 kcal/mol (~2× affinity loss, acceptable)
Confidence: High (trained on 1,000+ therapeutic antibody structures)
Issue 2: Viscosity (VH surface charge)
Mutation: K45Q (Lys → Gln)
Prediction: 30% reduction in charge patch size
Impact on stability: ΔΔG = +0.1 kcal/mol (neutral)
Confidence: Medium
Issue 3: Deamidation (CDR-H2 liability)
Mutation: G56A (Gly → Ala)
Prediction: 10× reduction in deamidation rate (Ala side chain restricts backbone)
Impact on affinity: Minimal (conservative mutation)
Confidence: High
Issue 4: Humanization (framework residues)
Mutations: A30S, R48K, I72V (revert to human germline)
Prediction: 40% reduction in T-cell epitope score
Impact on stability: Minimal
Confidence: High
Step 5: Design Optimized Variants
Create multiple variants to test in parallel:
Variant 1: Y99S only (test aggregation fix)
Variant 2: Y99S + K45Q (aggregation + viscosity)
Variant 3: Y99S + G56A (aggregation + chemical stability)
Variant 4: Y99S + K45Q + G56A + humanization (all fixes)
Orbion predicts performance for each variant:
Expected aggregation, viscosity, Tm, affinity
Decision: Express top 3 variants for experimental validation
Step 6: Experimental Validation (4-6 weeks)
Express variants:
Transient transfection in HEK293
Purify by Protein A
Yield: Measure expression titer
Biophysical characterization:
SEC-MALS: % monomer (aggregation)
Viscosity: Measure at 150 mg/mL
DSF: Tm for all domains
Binding assay (ELISA or SPR): Measure Kd (affinity)
Results example:
Variant 1: 98% monomer, affinity 1.5× loss (acceptable)
Variant 2: 97% monomer, viscosity 15 cP (excellent), affinity 2× loss
Variant 4: 99% monomer, viscosity 12 cP, <2% deamidation at 4 weeks/40°C, affinity 2.5× loss
Decision: Variant 4 is lead candidate (best overall developability, acceptable affinity)
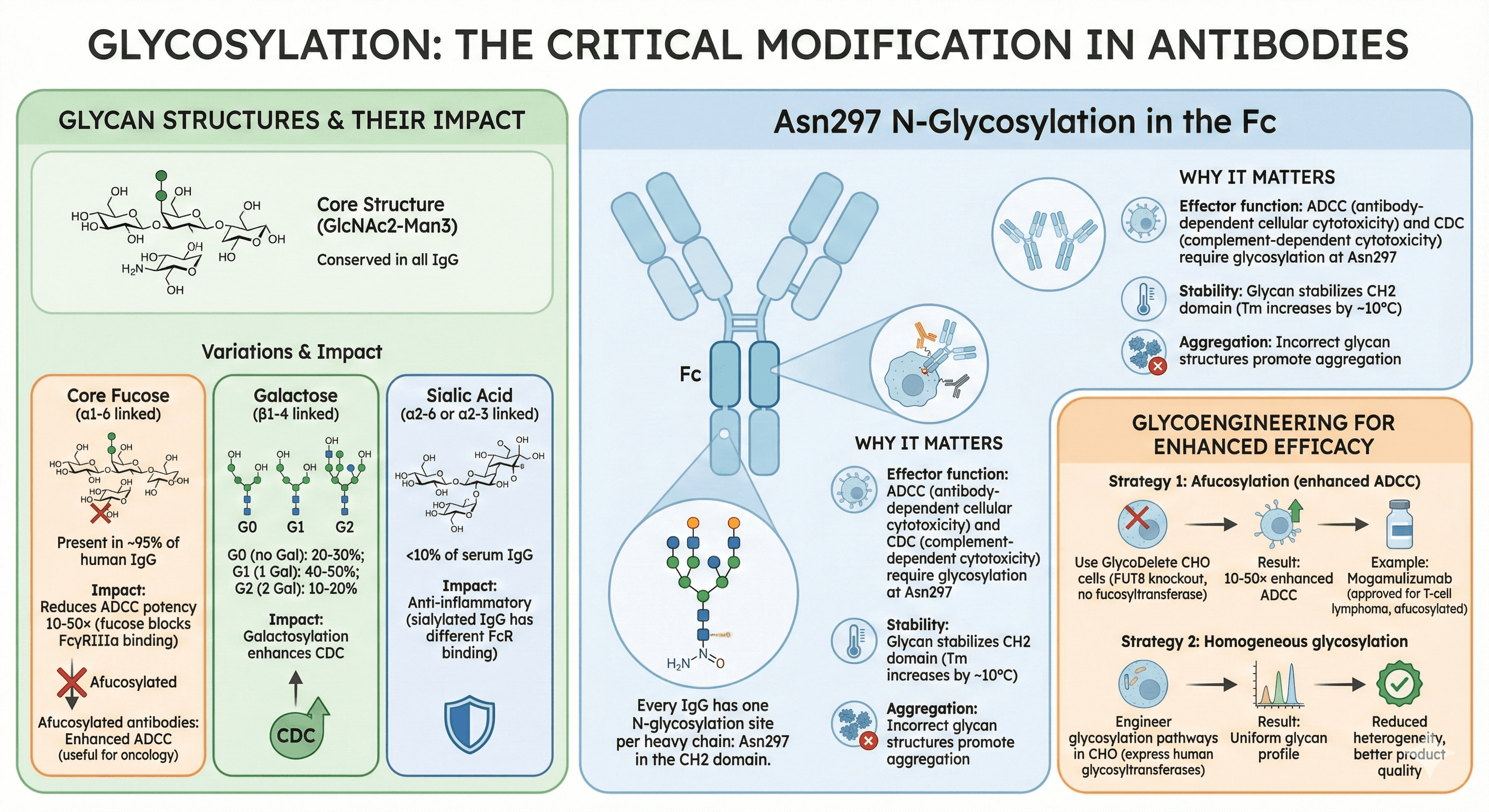
Glycosylation: The Critical Modification
Asn297 N-Glycosylation in the Fc
Every IgG has one N-glycosylation site per heavy chain: Asn297 in the CH2 domain.
Why it matters:
Effector function: ADCC (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity) and CDC (complement-dependent cytotoxicity) require glycosylation at Asn297
Stability: Glycan stabilizes CH2 domain (Tm increases by ~10°C)
Aggregation: Incorrect glycan structures promote aggregation
Glycan Structures and Their Impact
Core structure:
GlcNAc2-Man3 (core pentasaccharide, conserved in all IgG)
Variations:
Core fucose (α1-6 linked to core GlcNAc):
Present in ~95% of human IgG
Impact: Reduces ADCC potency 10-50× (fucose blocks FcγRIIIa binding)
Afucosylated antibodies: Enhanced ADCC (useful for oncology)
Galactose (β1-4 linked to core Man):
G0 (no Gal): 20-30%
G1 (1 Gal): 40-50%
G2 (2 Gal): 10-20%
Impact: Galactosylation enhances CDC
Sialic acid (α2-6 or α2-3 linked to Gal):
<10% of serum IgG
Impact: Anti-inflammatory (sialylated IgG has different FcR binding)
Glycoengineering for Enhanced Efficacy
Strategy 1: Afucosylation (enhanced ADCC)
Use GlycoDelete CHO cells (FUT8 knockout, no fucosyltransferase)
Result: 10-50× enhanced ADCC
Example: Mogamulizumab (approved for T-cell lymphoma, afucosylated)
Strategy 2: Homogeneous glycosylation
Engineer glycosylation pathways in CHO (express human glycosyltransferases)
Result: Reduced heterogeneity, better product quality
Predicting Glycosylation with Orbion's AstraPTM2
What it does:
Predicts N-glycosylation sites from sequence (Asn-X-Ser/Thr consensus)
Predicts which sites are actually glycosylated (not all consensus sequences are modified)
Flags unintended glycosylation sites in CDRs or frameworks
Why this matters:
Unintended glycosylation in CDRs adds heterogeneity (complicates analytics)
Low glycosylation efficiency at Asn297 may require expression system change (E. coli → mammalian)
Additional sites can be engineered for therapeutic purposes (mask aggregation hotspots)
Real Rescue Case Studies
Case Study 1: Anti-TNF Antibody Viscosity Rescue
Background:
Anti-TNF-α antibody for rheumatoid arthritis
High affinity (Kd = 0.3 nM), excellent neutralization
Problem: Viscosity 125 cP at 150 mg/mL (target <20 cP, failed Phase I)
Investigation (Orbion analysis):
Charge patch analysis: Large positive patch on VH (7 Lys/Arg), large negative patch on VL (5 Glu/Asp)
Strong electrostatic interactions drive self-association
Solution:
Orbion suggests 8 mutations to reduce charge patches
Design 4 variants: K50Q, K50Q+E52Q, K50Q+E52Q+K89Q, K50Q+E52Q+K89Q+R92Q
Results:
Variant 3 (triple mutant): Viscosity 18 cP at 150 mg/mL ✓
Affinity: Kd = 0.4 nM (1.3× loss, acceptable)
Outcome:
Re-entered Phase I with optimized antibody
Phase II completed successfully
Time saved: 6 months vs traditional trial-and-error
Cost saved: $15-25M
Case Study 2: Anti-HER2 Deamidation Liability Fix
Background:
Anti-HER2 antibody, high efficacy in vivo
Problem: 12% deamidation after 6 months at 4°C (shelf life issue)
Deamidation site: Asn55-Gly56 in CDR-H2
Deamidated antibody: 5× lower affinity
Solution:
Mutation: G56A (Gly → Ala)
Prediction: 10× reduction in deamidation rate
Results:
Deamidation at 6 months: <2% (acceptable)
Affinity: Unchanged (Gly → Ala is conservative)
Charge heterogeneity: Minimal
Outcome:
Achieved 24-month shelf life specification
IND approved
Impact: Avoided $50M+ program restart
Case Study 3: Anti-EGFR Aggregation Rescue
Background:
High affinity (Kd = 0.5 nM), potent cell killing
Problem: 15% aggregation at 100 mg/mL within 1 week
Investigation:
AGGRESCAN3D: Hydrophobic patch in CDR-H3 (residues 98-103: YYYGDY)
3 Tyr residues create 300 Ų hydrophobic surface
Solution:
Mutation: Y100S (Tyr → Ser in CDR-H3)
Prediction: 70% reduction in aggregation, ΔΔG binding = +0.8 kcal/mol (2× loss acceptable)
Results:
Affinity: Kd = 1.2 nM (2.4× loss, still excellent)
Solubility: Stable at 150 mg/mL for 6 months
Aggregation: <1% HMWS at shelf life
Outcome:
IND approved, entered Phase I
Lesson: One mutation rescued a $40M failed program
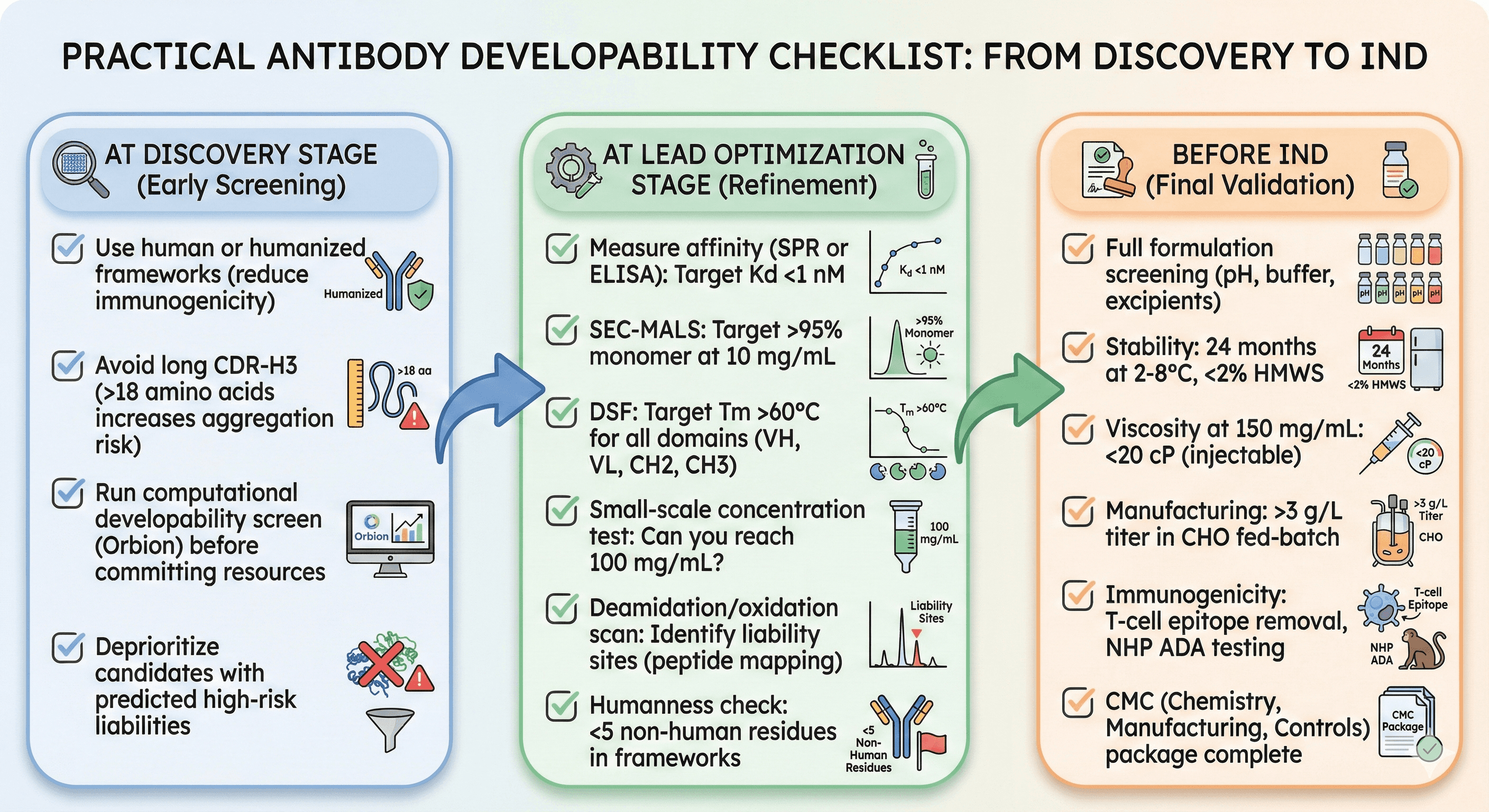
Practical Antibody Developability Checklist
At Discovery Stage
[ ] Use human or humanized frameworks (reduce immunogenicity)
[ ] Avoid long CDR-H3 (>18 amino acids increases aggregation risk)
[ ] Run computational developability screen (Orbion) before committing resources
[ ] Deprioritize candidates with predicted high-risk liabilities
At Lead Optimization Stage
[ ] Measure affinity (SPR or ELISA): Target Kd <1 nM
[ ] SEC-MALS: Target >95% monomer at 10 mg/mL
[ ] DSF: Target Tm >60°C for all domains (VH, VL, CH2, CH3)
[ ] Small-scale concentration test: Can you reach 100 mg/mL?
[ ] Deamidation/oxidation scan: Identify liability sites (peptide mapping)
[ ] Humanness check: <5 non-human residues in frameworks
Before IND
[ ] Full formulation screening (pH, buffer, excipients)
[ ] Stability: 24 months at 2-8°C, <2% HMWS
[ ] Viscosity at 150 mg/mL: <20 cP (injectable)
[ ] Manufacturing: >3 g/L titer in CHO fed-batch
[ ] Immunogenicity: T-cell epitope removal, NHP ADA testing
[ ] CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, Controls) package complete
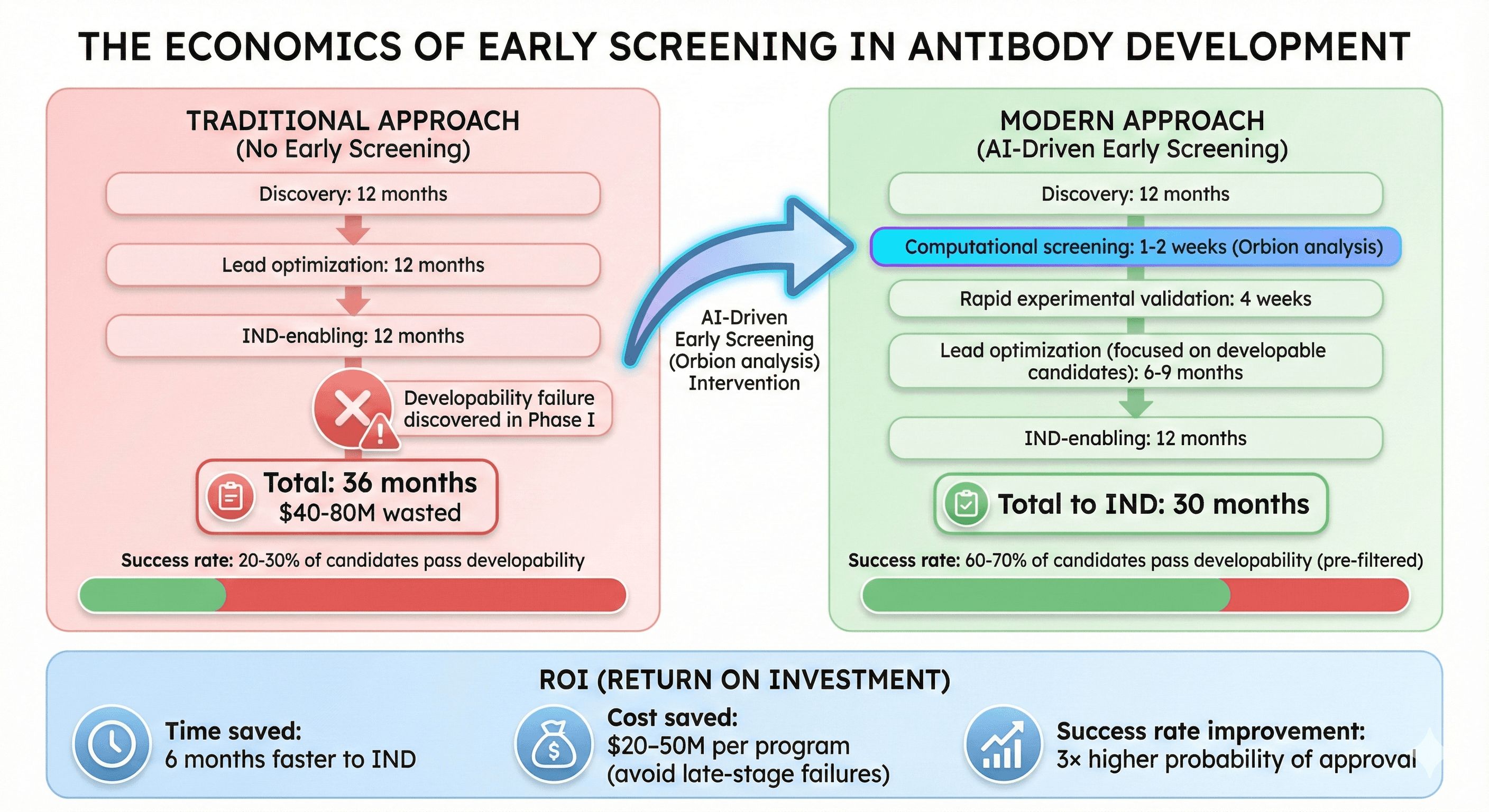
The Economics of Early Screening
Traditional Approach (No Early Screening)
Timeline:
Discovery: 12 months
Lead optimization: 12 months
IND-enabling: 12 months
Developability failure discovered in Phase I: Total 36 months, $40-80M wasted
Success rate: 20-30% of candidates pass developability
Modern Approach (AI-Driven Early Screening)
Timeline:
Discovery: 12 months
Computational screening: 1-2 weeks (Orbion analysis)
Rapid experimental validation: 4 weeks
Lead optimization (focused on developable candidates): 6-9 months
IND-enabling: 12 months
Total to IND: 30 months
Success rate: 60-70% of candidates pass developability (pre-filtered)
ROI:
Time saved: 6 months faster to IND
Cost saved: $20-50M per program (avoid late-stage failures)
Success rate improvement: 3× higher probability of approval
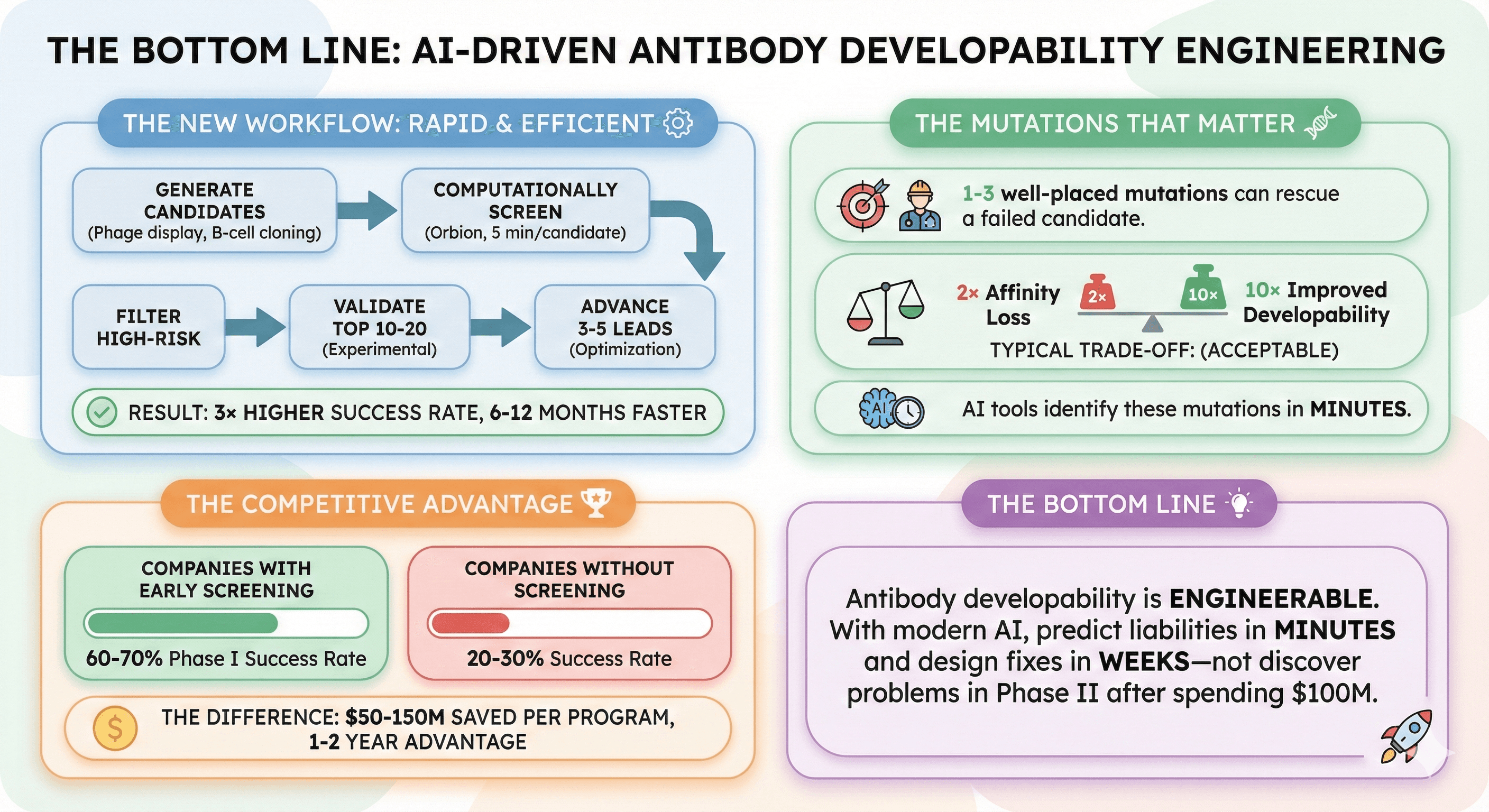
The Bottom Line
Antibody developability is engineerable. With modern AI tools, you can predict liabilities in minutes and design fixes in weeks—not discover problems in Phase II after spending $100M.
The new workflow:
Generate antibody candidates (phage display, B-cell cloning)
Computationally screen for developability (Orbion, 5 minutes per candidate)
Filter out high-risk candidates
Experimentally validate top 10-20
Advance 3-5 developable leads to optimization
Result: 3× higher success rate, 6-12 months faster
The mutations that matter:
1-3 well-placed mutations can rescue a failed candidate
Typical trade-off: 2× affinity loss for 10× improved developability (acceptable)
AI tools identify these mutations in minutes
The competitive advantage:
Companies using early developability screening: 60-70% Phase I success rate
Companies without screening: 20-30% success rate
The difference: $50-150M saved per program, 1-2 year advantage over competitors
Ready to Engineer Your Antibody for Success?
If you have an antibody candidate and want to optimize developability before investing in clinical trials, Orbion can help.
Orbion provides:
Aggregation hotspot prediction with specific mutation recommendations
Viscosity prediction and charge-balancing strategies
Thermal stability optimization (ΔΔG for all domains)
PTM liability detection (deamidation, oxidation, glycosylation)
Immunogenicity risk assessment with humanization suggestions
Complete developability scorecard in minutes

